Canon recently announced the launch of its "Ceramic 3D Printing Service" for the Chinese market.
Recently, Mohou.com understands that a new heavyweight player has been added to the field of ceramic 3D printing, and Canon recently announced the launch of "Ceramic 3D Printing Service" for the Chinese market.
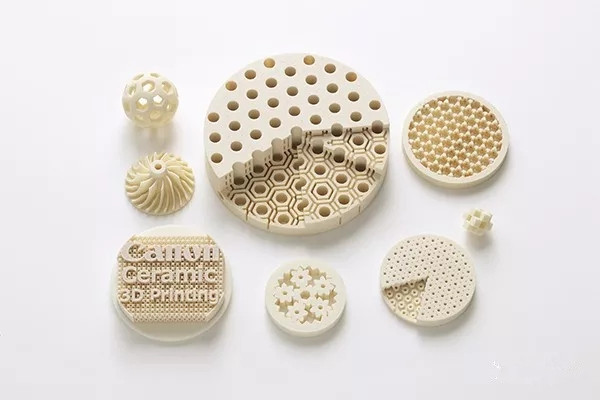

It is reported that Canon has developed ceramic composite powder materials (hereinafter referred to as "ceramic powder") with two substrates of alumina and silicon oxide, and boldly used SLM selective laser melting technology (hereinafter referred to as "SLM technology") to shape the ceramic powder. By combining ceramic powder with SLM technology (hereinafter referred to as "Canon Ceramic 3D Printing Technology"), Canon is able to produce complex-shaped ceramic parts in a short period of time.

△Canon's ceramic composite powder material
Pain points of ceramic 3D printing technology in the market
The traditional processing method of ceramics is to put the ceramic powder material into a mold to solidify and shape under pressure, then put it into a furnace to fire it, and finally grind the surface and other treatments to productize it; however, making a mold not only takes a certain amount of time, but also requires high costs; therefore, ceramic 3D printing technology came into being, and at present, the ceramic 3D printing technology on the market mainly contains four kinds:
● Selective laser melting technology: the ceramic 3D printing technology can be used to make ceramic parts.
● Selective laser melting technology: Ceramic powder materials are melted and molded by irradiating with laser.
●Binder injection technology: ceramic powder materials are laminated and molded by adhesive.
●Light curing technology: A mixture of resin and ceramic powder is molded layer by layer by irradiating it with ultraviolet light.
●Extrusion molding technology: Heated and melted ceramic powder material is extruded from a nozzle and stacked to form.
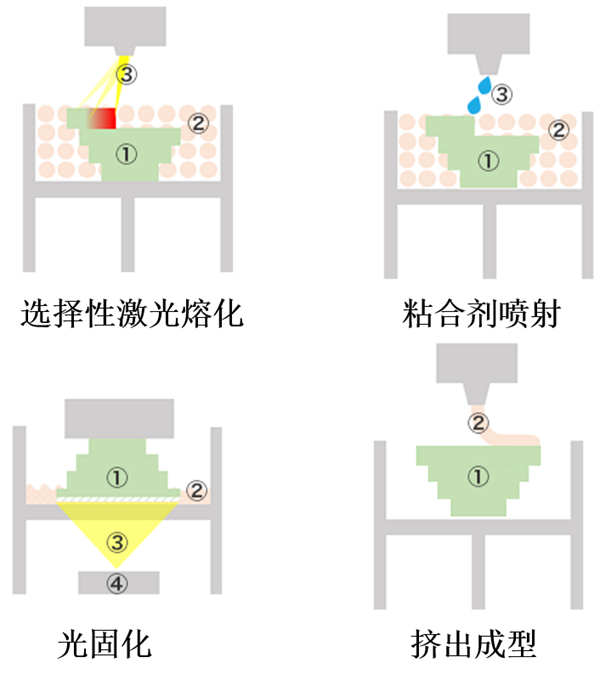
△The main ceramic 3D printing technologies currently on the market
Currently, the mainstream ceramic 3D printing technology on the market is light-curing technology: this technology requires mixing ceramic particles into photosensitive resin material to make a high solid content ceramic paste, then curing the photosensitive resin by ultraviolet light to mold, and after molding, the final ceramic parts are obtained through a degreasing and sintering process.
Due to the addition of photosensitive resin as a binder, the ceramic parts generally shrink about 15~20% during the degreasing and sintering process, and are prone to cracking during the sintering process. Therefore, to obtain accurate part dimensions, designers need to design with shrinkage in mind during the firing process, and there can be many challenges in making fine shapes and complex structures.
Canon Ceramic 3D Printing Technology
Canon ceramic 3D printing technology, using self-developed alumina ceramic powder with SLM technology, has solved the above-mentioned problems well and successfully realized the practicalization of high-fine ceramic 3D printing. Since the melting point of alumina ceramic powder is above 2000°C, it is difficult to melt by laser. Canon has added auxiliary materials to enhance the infrared absorption efficiency to lower the melting point to about 1700°C, and has been able to successfully realize ceramic 3D printing by SLM technology.
It is worth mentioning that Canon's ceramic powder does not contain resin, and no resin binder is added in the 3D printing process, so there is no need to consider the trouble of degreasing, which to a certain extent solves the problems of severe sintering shrinkage, difficulty in degreasing, and easy cracks that resin-containing ceramic materials generally face.
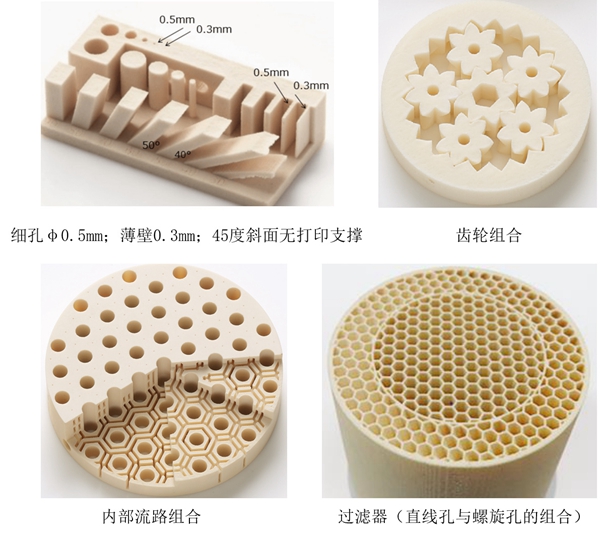

△Canon's ceramic 3D printing sample
It is reported that by using Canon's ceramic powder with SLM technology for 3D printing, the shrinkage of ceramic parts before and after sintering can be controlled within 2%, and the sintering time is shortened to about 50 hours, which can maintain a production accuracy of ±0.8% and stable processing quality.
Canon's ceramic 3D printing technology can not only produce complex structures such as cavities, honeycombs, and hollow flow paths, but also break through the limitations of previous shapes to a certain extent, allowing the molding of fine holes of φ0.5mm, thin-walled structures of 0.4mm, and thick-walled structures up to 25mm thick (wall thickness may vary depending on the shape).
In general, Canon's 3D ceramic printing technology has the following features.
● Saving time and cost by eliminating the need for molds.
● High temperature, abrasion, corrosion and insulation resistance.
● Suitable for complex structures such as cavities, honeycombs, and hollow flow paths.
● Fine hole, thin-walled and thick-walled shapes can be realized.
● Small shrinkage deformation, production accuracy ±0.8%.
● Maximum molding size 240*240*240mm.
● One piece can be made, short production cycle .
It is understood that Canon has started to launch ceramic 3D printing service in the Chinese market, which can 3D print ceramics according to the drawings provided by users and provide finished products to users; this ceramic 3D printing service is expected to be applied to many industrial fields such as aerospace, semiconductor, medical equipment, automobile manufacturing, precision instruments, scientific research and development.







